Can roots tourism build social justice? A case study of travellers to Ghana provides insights
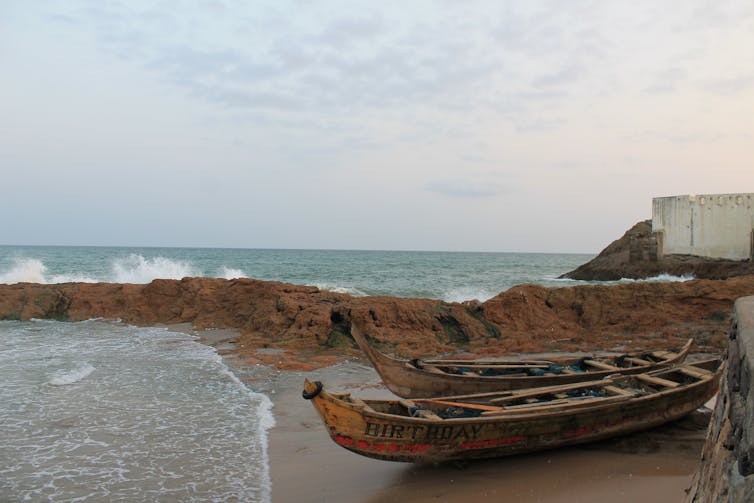


The view from the dungeon of the Cape Coast Castle.
Alana Dillette
In fact, Ghana, which has been a leader in connecting this diaspora to its African roots through tourism, commemorated the life of Floyd with a memorial service in Accra. The service was arranged by Ghana’s Year of Return committee, in partnership with the African Union of Diasporan Forum.
The Year of Return – 2019 – was a tourism campaign to commemorate the 400th anniversary of the first slave ship landing in America. It was an instance of “roots tourism”, which appeals to travellers to visit a destination on the basis of their ancestry.
Beyond the education and personal transformation that many travellers gain from this type of tourism, could it also be an opportunity for racial reconciliation?
My study of one recent group of African American roots travellers to Ghana suggests this may be a possibility. The study explored how the trip affected these travellers’ sense of identity and their commitment to social justice initiatives.
Exploring roots in Ghana
In August 2018, I joined a group of 10 African American travellers on a 10-day trip to Ghana where we visited historical sights, as well as cities, villages and nature preserves. I interviewed the travellers before and after the trip, in addition to conducting observations and a focus group during the trip. I asked them about their expectations of the journey and how the experience had affected their identity. I also asked if it made them more likely to participate in social justice activities such as protesting, getting involved with social justice organisations in their communities and speaking up about social injustices in their professions.
Travellers revealed to me that the trip helped them to conceptualise slavery differently, and this led them to a deeper understanding of race relations in the United States. For example, one traveller said that prior to visiting Ghana, they felt a “certain anger towards white people”. But visiting Ghana and specifically, the Cape Coast dungeon exposed them to learn more about all of the actors in slavery – (white) Europeans and (black) Africans.
Read more: Ghana hopes 'Year of Return' will boost tourism. But caution is needed
Travellers also shared how the trip helped them to understand more deeply their identity as both African and American. For example, one participant said:
I have these identifiable characteristics about me that link me to this place. I hope to go home and be able to exude that like a light off me, without being afraid or ashamed; we shouldn’t be fearful of who we really are.
This quote exemplifies how identity formation through roots travel can lead to a form of reconciliation within travellers themselves.
Another traveller said they realised after the trip that roots tourism, if curated well, could be an avenue for cross-racial communication and understanding. They said they had noticed a clear difference between white and black tour groups at the Cape Coast dungeon. One was more romanticised, and one highlighted more of the horrific details of slavery.
This traveller said the romanticised experience was common at many former slave plantation heritage tourism sites in the US. These types of narratives only perpetuate experiences reminiscent of the Jim Crow era. But if transformed, these experiences both in Ghana and the US could act as a platform for racial reconciliation.
One traveller described their own internal racial reconciliation by saying:
We are all human. I wish that we lived in a world that could really and truly embrace that, but we don’t. So, for now, I continue trying to spread the love and be unashamed about who I am, which is a mixture of so many things, some of which do originate in Africa, and I am proud of that now.
Making peace
These types of experiences through roots tourism represent an opportunity for the creation of peace and reconciliation. Travellers can learn together about the collective emotional trauma resultant from slavery, the misinformation that is often passed down about slavery and how these issues can be discussed openly.
Travel and tourism are not often linked to social justice. But the research shows that tourism does in fact provide a platform for this. Travellers in my study said their trip to Ghana empowered them to make changes towards social equity in their professional and personal lives. They described actionable change along with expanded mindsets. For example, one traveller mentioned getting involved with empowering black musicians in their community. Another started contributing financially to empower female business owners in Ghana.
Read more: Ghana's Year of Return 2019: traveler, tourist or pilgrim?
Roots travel experiences also shine a light on the continued everyday racism that people face as a trickle-down effect of slavery. Participants described how societal racism in the US had made an impact on their lives, and how travelling to Ghana had emboldened them to search for clarity of identity and self, as well as social equality.
The research already shows that tourism can promote peace, transformation and cross-cultural understanding. But it’s a good time to ask how the travel and tourism industry has contributed to racism and how that can change.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Source: The Conversation Africa

The Conversation Africa is an independent source of news and views from the academic and research community. Its aim is to promote better understanding of current affairs and complex issues, and allow for a better quality of public discourse and conversation.
Go to: https://theconversation.com/africaAbout Alana Dillette
Alana Dillette is Assistant Professor. L. Robert Payne School of Hospitality and Tourism Management, Tourism RESET, San Diego State University.Related
New GenG Engage app tackles gender-based violence in SA 2 days Entries open for WTM Africa Responsible Tourism Awards 20 Jan 2025 Zambia opens doors to 53 countries with new visa waiver 20 Dec 2024 Key trends defining the future of African hospitality in 2025 19 Nov 2024 Nelson Mandela Foundation names Dr Naledi Pandor as new chair 23 Sep 2024 SADC Tourism Alliance: Southern Africa remains low-risk for mpox 21 Aug 2024